Graph Algorithms
Single Source Shortest Paths
Bellman-Ford Algorithm
- detect negative loop
- relax edges for
- see all vertexes in each loop
- based on triangle inequality
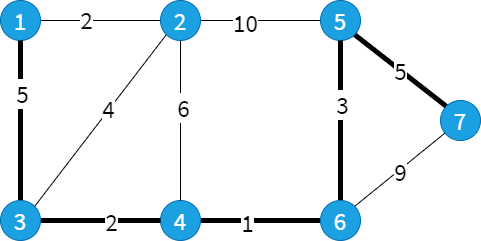
test1.txt
7 10 1 7
1 2 2
1 3 5
2 3 4
2 4 6
2 5 10
3 4 2
4 6 1
5 6 3
5 7 5
6 7 9
16
C++
#include <fstream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
#define MAX_N 10'000
#define MAX_K 10'000
#define INF 1'000'000'000
using namespace std;
struct Edge {
int u, v, weight;
};
int N, K, S, G;
int dist[MAX_N], path[MAX_N];
Edge E[MAX_K];
void init(int s) {
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
dist[i] = INF;
path[i] = -1;
}
dist[s] = 0;
}
void relax(int u, int v, int weight) {
if (dist[v] > dist[u] + weight) {
dist[v] = dist[u] + weight;
path[v] = u;
}
}
bool bellman_ford() {
for (int i = 0; i < N - 1; ++i) {
for (auto e : E) {
relax(e.u, e.v, e.weight);
}
}
for (auto e : E) {
if (dist[e.v] > dist[e.u] + e.weight) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
void print_path(int s, int v) {
if (s == v) {
printf("%d", s + 1);
} else if (v < 0) {
printf("\n No path");
} else {
print_path(s, path[v]);
printf("->%d", v + 1);
}
}
int main() {
ifstream ifs("../testset/single_source_shortest_path/test1.txt");
ifs >> N >> K >> S >> G;
--S;
--G;
for (int i = 0; i < K * 2; i += 2) {
int u, v, weight;
ifs >> u >> v >> weight;
--u;
--v;
E[i] = Edge{u, v, weight};
E[i + 1] = Edge{v, u, weight};
}
init(S);
if (bellman_ford()) {
printf("dist=%d\n", dist[G]);
printf("path=");
print_path(S, G);
printf("\n");
} else {
printf("detect negative loop\n");
}
}
// dist=16
// path=1->3->4->6->5->7
Python
INF = float('inf')
def ns(f):
return next(f).strip()
class Edge:
def __init__(self, u, v, weight):
self.u = u
self.v = v
self.weight = weight
with open("../testset/single_source_shortest_path/test1.txt", 'r') as f:
N, K, S, T = map(int, ns(f).split())
S -= 1
T -= 1
E = []
for _ in range(K):
u, v, weight = map(int, ns(f).split())
u -= 1
v -= 1
E.append(Edge(u, v, weight))
E.append(Edge(v, u, weight))
dist = [INF] * N
dist[S] = 0
path = [-1] * N
def relax(u, v, weight):
global dist, path
if dist[v] > dist[u] + weight:
dist[v] = dist[u] + weight
path[v] = u
def bellman_ford():
# return True if the graph has negative loops.
for _ in range(N - 1):
for e in E:
relax(e.u, e.v, e.weight)
for e in E:
if dist[e.v] < dist[e.u] + e.weight:
return False
return True
def _print_path(s, v):
if s == v:
print(s + 1, end='')
elif v < 0:
print('\nNo path', end='')
else:
_print_path(s, path[v])
print(f"->{v + 1}", end='')
def print_path(s, v):
_print_path(s, v)
print()
bellman_ford()
print(f"shortest distance={dist[T]}")
print("shortest path=", end='')
print_path(S, T)
# shortest distance=16
# shortest path=1->3->4->6->5->7
Dijkstra's Algorithm
- -> (used heap queue)
- use priority queue
- see only the most nearest vertex
C++
#include <fstream>
#include <queue>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
#define MAX_N 10'000
#define MAX_K 10'000
#define INF 1'000'000'000
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> P;
struct Edge {
int u, v, weight;
Edge(int u, int v, int weight) : u(u), v(v), weight(weight) {}
};
int N, K, S, T;
vector<Edge> G[MAX_N];
int dist[MAX_N], path[MAX_N];
void init(int s) {
fill(dist, dist + N, INF);
fill(path, path + N, -1);
dist[s] = 0;
}
void dijkstra(int s) {
init(s);
priority_queue<P, vector<P>, greater<P>> q;
q.push(P(0, s));
while (!q.empty()) {
P p = q.top();
q.pop();
int u = p.second;
if (dist[u] < p.first) {
continue;
}
for (auto e : G[u]) {
if (dist[e.v] > dist[u] + e.weight) {
// relax
dist[e.v] = dist[u] + e.weight;
path[e.v] = u;
q.push(P(dist[e.v], e.v));
}
}
}
}
void _print_path(int s, int v) {
if (s == v) {
printf("%d", s + 1);
} else if (v < 0) {
printf("No path\n");
} else {
_print_path(s, path[v]);
printf("->%d", v + 1);
}
}
void print_path(int s, int v) {
_print_path(s, v);
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
ifstream ifs("../testset/single_source_shortest_path/test1.txt");
ifs >> N >> K >> S >> T;
--S;
--T;
for (int i = 0; i < K; ++i) {
int u, v, weight;
ifs >> u >> v >> weight;
--u;
--v;
G[u].emplace_back(u, v, weight);
G[v].emplace_back(v, u, weight);
}
dijkstra(S);
printf("shortest distance=%d\n", dist[T]);
printf("shortest path=");
print_path(S, T);
}
// shortest distance=16
// shortest path=1->3->4->6->5->7
Python
from heapq import heapify, heappop, heappush
INF = float('inf')
def ns(f):
return next(f).strip()
class Edge:
def __init__(self, u, v, weight):
self.u = u
self.v = v
self.weight = weight
with open("../testset/single_source_shortest_path/test1.txt", 'r') as f:
N, K, S, T = map(int, ns(f).split())
S -= 1
T -= 1
G = [[] for _ in range(N)]
for _ in range(K):
u, v, weight = map(int, ns(f).split())
u -= 1
v -= 1
G[u].append(Edge(u, v, weight))
G[v].append(Edge(v, u, weight))
dist = [INF] * N
dist[S] = 0
path = [-1] * N
def dijkstra():
global dist, path
q = [[0, S]]
heapify(q)
while len(q) > 0:
p = heappop(q)
u = p[1]
if dist[u] < p[0]:
continue
for e in G[u]:
if dist[e.v] > dist[u] + e.weight:
dist[e.v] = dist[u] + e.weight
path[e.v] = u
heappush(q, [dist[e.v], e.v])
def _print_path(s, v):
if s == v:
print(s + 1, end='')
elif v < 0:
print('\nNo path', end='')
else:
_print_path(s, path[v])
print(f"->{v + 1}", end='')
def print_path(s, v):
_print_path(s, v)
print()
dijkstra()
print(f"shortest distance={dist[T]}")
print("shortest path=", end='')
print_path(S, T)
# shortest distance=16
# shortest path=1->3->4->6->5->7
All Pairs Shortest Paths
Warshall-Floyd Algorithm
- use DP to consider a path from to is through or not
- which more shorter is path through or not
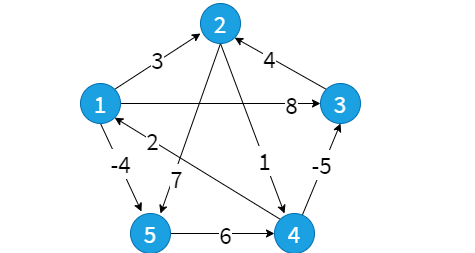
test1.txt
5 9
1 2 3
1 3 8
1 5 -4
2 4 1
2 5 7
3 2 4
4 1 2
4 3 -5
5 4 6
0 1 -3 2 -4
3 0 -4 1 -1
7 4 0 5 3
2 -1 -5 0 -2
8 5 1 6 0
C++
#include <algorithm>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX_N 1'000
#define INF 1'000'000'000
using namespace std;
int N, K;
int d[MAX_N][MAX_N];
void warshall_floyd() {
for (int k = 0; k < N; ++k) {
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j) {
d[i][j] = min(d[i][j], d[i][k] + d[k][j]);
}
}
}
}
int main() {
ifstream ifs("../testset/all_pairs_shortest_path/test1.txt");
ifs >> N >> K;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j) {
if (i == j) {
d[i][j] = 0;
} else {
d[i][j] = INF;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < K; ++i) {
int u, v, weight;
ifs >> u >> v >> weight;
--u;
--v;
d[u][v] = weight;
// if non-direction graph add d[v][u]
// d[v][u] = weight;
}
warshall_floyd();
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j) {
printf("%d ", d[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
Python
INF = float('inf')
def ns(f):
return next(f).strip()
with open("../testset/all_pairs_shortest_path/test1.txt", 'r') as f:
N, K = map(int, ns(f).split())
d = [[0 if i == j else INF for j in range(N)] for i in range(N)]
for _ in range(K):
u, v, weight = map(int, ns(f).split())
u -= 1
v -= 1
d[u][v] = weight
# if non-direction graph add d[v][u]
# d[v][u] = weight
def warshall_floyd():
global d
for k in range(N):
for i in range(N):
for j in range(N):
d[i][j] = min(d[i][j], d[i][k] + d[k][j])
warshall_floyd()
for _d in d:
print(' '.join(map(str, _d)))
MST: Minimum Spanning Tree
Kruscal's Algorithm
- be similar to Bellman-Ford Algorithm
- use Union-Find Tree
- add vertexes of the min weight edge into tree repeatedly if the tree doesn't include the vertexes
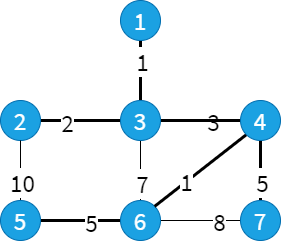
test1.txt
7 9
1 3 1
2 3 2
2 5 10
3 4 3
3 6 7
4 6 1
4 7 5
5 6 5
6 7 8
17
C++
#include <algorithm>
#include <fstream>
#include <memory.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX_N 10'000
#define MAX_K 10'000
using namespace std;
struct Edge {
int u, v, weight;
};
int N, K, ans;
int par[MAX_N], rnk[MAX_N]{};
Edge E[MAX_K];
void init() {
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
par[i] = i;
}
}
int find(int u) {
if (par[u] == u) {
return u;
}
return par[u] = find(par[u]);
}
void unite(int u, int v) {
u = find(u);
v = find(v);
if (u == v) {
return;
}
if (rnk[u] < rnk[v]) {
par[u] = v;
} else {
par[v] = u;
if (rnk[u] == rnk[v]) {
++rnk[u];
}
}
}
bool same(int u, int v) { return find(u) == find(v); }
int kruscal() {
int res = 0;
sort(E, E + K, [](const Edge &e1, const Edge &e2) { return e1.weight < e2.weight; });
init();
for (auto e : E) {
if (!same(e.u, e.v)) {
res += e.weight;
unite(e.u, e.v);
}
}
return res;
}
int main() {
ifstream ifs("../testset/minimum_spanning_tree/test1.txt");
ifs >> N >> K;
for (int i = 0; i < K; ++i) {
int u, v, weight;
ifs >> u >> v >> weight;
E[i] = Edge{--u, --v, weight};
}
ans = kruscal();
printf("%d\n", ans);
}
Python
def ns(f):
return next(f).strip()
class Edge:
def __init__(self, u, v, weight):
self.u = u
self.v = v
self.weight = weight
with open("../testset/minimum_spanning_tree/test1.txt", 'r') as f:
N, K = map(int, ns(f).split())
E = []
for _ in range(K):
u, v, weight = map(int, ns(f).split())
E.append(Edge(u - 1, v - 1, weight))
par = [i for i in range(N)]
rnk = [0] * N
def find(u):
global par
if par[u] == u:
return u
par[u] = find(par[u])
return par[u]
def unite(u, v):
global par, rnk
u = find(u)
v = find(v)
if u == v:
return
if rnk[u] < rnk[v]:
par[u] = v
else:
par[v] = u
if rnk[u] == rnk[v]:
rnk[u] += 1
def same(u, v):
return find(u) == find(v)
def kruscal():
res = 0
E.sort(key=lambda x: x.weight)
for e in E:
if not same(e.u, e.v):
res += e.weight
unite(e.u, e.v)
return res
ans = kruscal()
print(ans)
Prim's Algorithm
- be similar to Dijkstra's Algorithm
- use priority queue ->
- add vertex having the shortest distance from added vertexes in the tree into tree repeatedly
C++
#include <fstream>
#include <queue>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <utility>
#include <vector>
#define MAX_N 10'000
#define MAX_K 10'000
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> P;
struct Edge {
int u, v, weight;
Edge(int u, int v, int weight) : u(u), v(v), weight(weight) {}
};
int N, K, ans;
vector<Edge> G[MAX_N];
bool used[MAX_N]{};
int prim() {
int res = 0;
used[0] = true;
priority_queue<P, vector<P>, greater<P>> q;
for (auto e : G[0]) {
q.push(P(e.weight, e.v));
}
while (!q.empty()) {
P p = q.top();
q.pop();
int u = p.second;
if (used[u]) {
continue;
}
used[u] = true;
res += p.first;
for (auto e : G[u]) {
if (!used[e.v]) {
q.push(P(e.weight, e.v));
}
}
}
return res;
}
int main() {
ifstream ifs("../testset/minimum_spanning_tree/test1.txt");
ifs >> N >> K;
for (int i = 0; i < K; ++i) {
int u, v, weight;
ifs >> u >> v >> weight;
--u;
--v;
G[u].emplace_back(u, v, weight);
G[v].emplace_back(v, u, weight);
}
ans = prim();
printf("%d\n", ans);
}
Python
from heapq import heapify, heappop, heappush
def ns(f):
return next(f).strip()
class Edge:
def __init__(self, u, v, weight):
self.u = u
self.v = v
self.weight = weight
with open("../testset/minimum_spanning_tree/test1.txt", 'r') as f:
N, K = map(int, ns(f).split())
G = [[] for _ in range(N)]
for _ in range(K):
u, v, weight = map(int, ns(f).split())
u -= 1
v -= 1
G[u].append(Edge(u, v, weight))
G[v].append(Edge(v, u, weight))
used = [False] * N
def prim():
global used
res = 0
used[0] = True
q = [[e.weight, e.v] for e in G[0]]
heapify(q)
while len(q) > 0:
p = heappop(q)
u = p[1]
if used[u]:
continue
used[u] = True
res += p[0]
for e in G[u]:
if not used[e.v]:
heappush(q, [e.weight, e.v])
return res
ans = prim()
print(ans)